The "Victorian Era": Inspirational origins.
(Note: This article is a work in progress. From time to time new information will be added and other parts changed.)
The term "Victorian" is used in the context of Steampunk and Retro-futurism to define a time period and an aesthetic, not a specific culture.
It was a period of economic, colonial and industrial consolidation within Europe, as well as global expansion into Asia and Africa, making the British Empire the largest empire in history. This lead to;
Across the globe European colonialists were exploring the interiors of what to them were new lands, colonising new territories, building railways, seeking gold and more.
It was the period immediately following the Industrial Revolution (1760 to 1840). A period which saw advances in important technologies:
This era saw huge transformations in culture. These came about as a knock on effect from the Industrial Revolution. People began to have more time and more money. This lead to more time to dream and the means with which to make things happen.
The term "Victorian" is used in the context of Steampunk and Retro-futurism to define a time period and an aesthetic, not a specific culture.
Victorian era
The Victorian era was the period of the reign of Queen Victoria, Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Empress of India. Victoria's reign was from the 20th Jun 1837 until the 22nd January 1901. Within the United Kingdom and many parts of the world it was a period of peace (Pax Britannica), prosperity, and refined sensibilities. The British Empire became the global hegemonic power, adopting the role of global police force.It was a period of economic, colonial and industrial consolidation within Europe, as well as global expansion into Asia and Africa, making the British Empire the largest empire in history. This lead to;
- Exploration and Colonial Expansion
- Industrialisation
- Cultural Transformation
It was also a period that saw the development of many key areas that would form the foundations of the modern world (including the use of mass production in manufacturing, extensive urbanisation, telecommunications, office life and mass-transit).
It really was the dawning of what we now know as the modern world.
It really was the dawning of what we now know as the modern world.
Exploration and Colonial Expansion
(Note: This was a period of rabid colonial expansion. As such it was also a period of major conflict between colonisers and indigenous peoples. This article is not intended to in any way condone or glorify any of the darker aspects of this period. The information is provided for reference only.)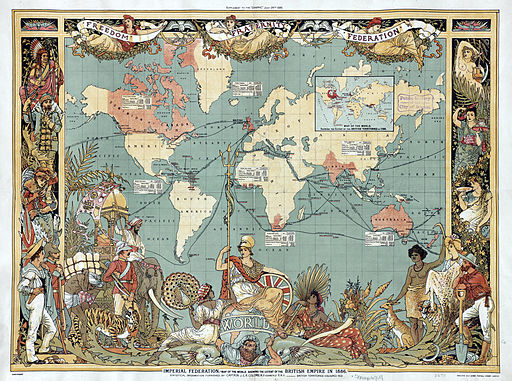 |
| Imperial Federation, Map of the World Showing the Extent of the British Empire in 1886 (levelled) Walter Crane [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
Across the globe European colonialists were exploring the interiors of what to them were new lands, colonising new territories, building railways, seeking gold and more.
- America, North - "Wild West" or "Old West" (1783 - 1920)
- American Civil War (1861–1865)
- The Californian Gold Rush
- The Oregon Trail
- The Pony Express and Telegraph
- Transcontinental Railway
- America, South
- The War of the Triple Alliance (Paraguayan War) (1865 -1870)
- War of the Pacific (1879 - 1884)
- The Spanish-American War (1898)
- Africa - "The Scramble for Africa" (1881 - 1914)
- European exploration of the African interior began at the end of the 18th century
- David Livingstone and H. M. Stanley mapped vast areas of Southern and Central Africa
- Richard Burton, John Speke and James Grant located the great central lakes and the source of the Nile
- Construction of the Suez Canal
- The Boer War
- Asia -
- China -
- Opium Wars (1839 - 1860)
- First Sino-Japanese War (1894 - 1895)
- East India Company
- India -
- British Raj (1858 - 1947)
- East India Company
- East Indies (Indonesia) - Dutch East Indies (1815 - 1949)
- Australia - colonial period (1788 - 1901)
- Gold rushes
- Expansion into Australia's interior by European explorers
- The Bushrangers
- Australian Democracy, Suffrage and Federation
- Etc.
Industrialisation
 |
Levels of air pollution rose during the Industrial Revolution, sparking the first modern |
It was the period immediately following the Industrial Revolution (1760 to 1840). A period which saw advances in important technologies:
Textiles
Mechanised cotton spinning, powered by steam or water, increased the output of a worker;- The power loom increased a workers output by a factor of 40.
- The cotton gin increased a workers output by a factor of 50.
Steam power
Steam engine efficiency increased, allowing them to use between one fifth and one tenth as much fuel. The development of the high pressure engine (with a higher power to weight ration) allowed for the use of steam in transport.Iron making
The substitution of coke for charcoal;- lowered the fuel cost for pig and wrought iron production
- allowed for larger blast furnaces, making it more ecomical
Other advances like the blowing cylinder, puddling process, rolling mill and hot blast, increased fuel efficiency, productivity and economic returns.
Invention of machine tools
The first machine tools were invented, including the screw cutting lathe, cylinder boring machine and milling machine.Cultural Transformation
 |
The Crystal Palace held the Great Exhibition of 1851 By J. McNeven - collections.vam.ac.uk, Public Domain, Link |
Some of the major cultural changes included;
- High Culture
- This period saw the increase in significance of Gothic Revivial architecture, leading to a Battle of Styles between Gothic and Classical.
- The Great Exhibition of 1851, the first World's Fair, had the Crystal Palace at its centre. While its design was initially condemned as the very model of mechanical dehumanisation, it later came to represent the prototype of Modern architecture.
- Victorian art was heavily influenced by the emergence of photography, showcased at the Great Exhibition.
- The middle-class
- With industrialisation came the rapid grown of the middle class, which in turn influenced the social strata, cultural norms, lifestyles, values and morality.
- As real wages increased, work hours decreased, causing an increase in leasure time.
- Suffragettes
- The changes in socio-economic conditions of this new age also brought with it the rise of the Suffragettes (Suffragists in the US). These were mostly women from the upper and middle classes who were frustrated with their social and economic situation. Their actions ultimately lead to women having the right to vote.
- Trade Unions
- With industrialisation and changes in wages and work hours and conditions came the unification of the workers. Workers joined together to collectively bargain for their rights and work conditions. These loose organisations became Trade Unions, and while initially illegal, they were widely legalised through the later part of the 19th century.




Comments
Post a Comment